Digital Twins — Redefining the Ways Industries Work
Digital twin technology is revolutionizing industries by enhancing strategic decision-making, improving product performance, and user experience.
June 4, 2024

In the rapidly progressing landscape of Industry 4.0, digital twin technology stands at the forefront of innovation, revolutionizing the way industries operate. Organizations are implementing digital twins to make better strategic decisions based on visions provided by the digital twins, get better perceptions regarding product performance and user experience, and more.
The impact of digital twin technology is set to expand significantly, with an increasing number of organizations incorporating it with the next decade. According to Gartner, 40% of large organizations could be using digital twins by 2027.
Studies have found that digital twin technology has the ability to increase revenue by 10% and improve product quality by 25%. But those aren't the only benefits digital twins can bring to organizations and industries, and shown by following statistics:
Digital twin solutions take 3 minutes or less to find actionable asset information.
Digital twin solutions increase staff productivity by 10%.
These solutions allow a 30% or more reduction in unplanned downtime.
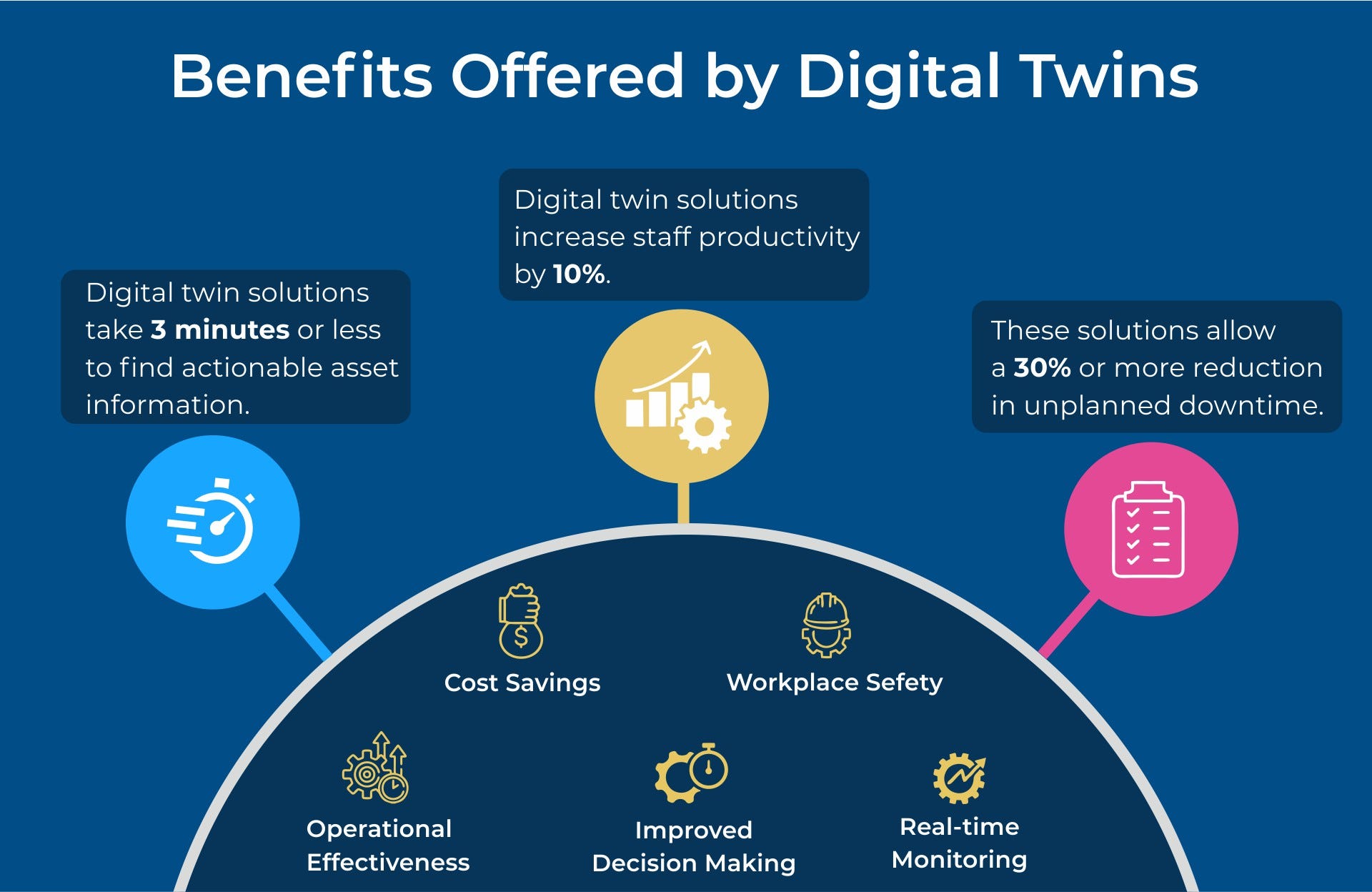
Digital twins provide a number of benefits to the users.
Inaccurate data can cost a fortune. And so will late decisions. Digital twins offer a powerful solution, extending far beyond mere technical assistance.
Digital Twins in a Nutshell
A digital twin is a virtual representation of an object or system designed to replicate a physical object precisely. In other words, a digital twin serves as a proxy for the current condition of anything it represents, via the exchange of data in real time. Real-time data from digital twin solutions unlock the visibility of current progress or challenges and plans ways to resolve or improve them.
While the concept of a digital twin is not new, its first practical use occurred in 2010 when the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) implemented it, in an attempt to improve the physical-model simulation of spacecraft.
From its celestial beginnings, the concept of the digital twin started to evolve and transform the industrial sector. It has also become a part of our daily lives through the use of digital maps on our smartphones and fitness bands that collect real-time data of users' heart rate, temperature, pulse rates, sleep patterns, etc., and offer personalized workouts.
Digital Twins Are Gaining in Popularity
Since digital twin technology is still in the nascent stage, only a few industries — like construction, manufacturing, and transportation — are currently embracing this technology.
However, it is rapidly gaining traction. In 2021, the global market of digital twins was $7.2 billion, and it is expected to jump to $92 billion by 2028, a whopping annual growth of 44%. The primary reasons for this growth are the benefits that digital twin technologies provide to organizations and industries that adopt them. As advancements in the technology continue and it integrates with trends like artificial intelligence and the internet of things (IoT), digital twins will become even more popular.
Digital Twins Being Put into Practice
Take Xovis' digital twin system in the form of its passenger flow management system (PFMS). Xovis, a software company offering people flow and people counting solutions, in April deployed a PFMS at a busy checkpoint at Vancouver International Airport to analyze real-time data on passenger flow. This digital twin acts as a virtual replica of a security checkpoint, allowing optimized staffing, reduced wait times, and an improved passenger flow and travel experience. This is not the first time Xovis has deployed a digital twin — the company has deployed digital twin solutions in the form of a PFMS to more than 110 airports globally.
The logistics industry isn't far behind in reaping the benefits of digital twins. Ford in April adopted digital twins to boost logistics efficiency. The automobile giant is applying digital twin technology for inbound material flow, integration of real-time location services into transport and yard management, and data management in logistics. The group's adoption of digital twins will be beneficial in several ways, including improving overall efficiency.
In the world of construction and infrastructure development, the digital revolution is reshaping traditional practices. The use of digital twins with construction projects promises to add precision and efficiency. For instance, the National Geospatial Policy (NGP) aims to create digital twins of India's major cities and towns by 2035 to mirror urban landscapes and physical assets. In alignment with this, the Survey of India (SOI) — the national mapping agency and custodian of India's map — has signed an agreement with Indian private mapping company Genesys International to prepare three-dimensional maps and digital twins of several cities and towns, which can be used in a variety of planning applications. The deployment of digital twin technologies will help with traffic planning and real estate development, and also help solve environmental challenges like floods, etc., by creating maps and more.
The Transformative Future of Digital Twins
There are a couple of numbers that underscore the need for organizations to embrace technologies like digital twins that can provide real-time data that can help avoid costly consequences.
Those aren't the only statistics that show that digital twins today are not just "nice-to-have," but an expectation. Real-time data in context means precise, accurate, and immediate decision-making.
The growth projections from different firms are impressive. For example, IDC forecasts that by 2027, 35% of G2000 companies will employ supply chain orchestration tools featuring digital twin capabilities, boosting the supply chain responsiveness by 15%. Stratview Research estimates that the global digital twin market will cross a whooping $92 billion by 2028, from just $10 billion in 2022.
Digital twin technology is in a nascent stage, meaning that its widespread adoption is yet to be seen. Its novelty, however, is just one of the reasons holding it back. Other challenges include a lack of regulations and standards, a lack of trained technicians, inaccurate presentation, and data security concerns.
The deeper that industries delve into the capabilities of digital twin technology, the higher the transformative applications and advancements in the years to come. When combined with other technologies including augmented reality, virtual reality, and additive manufacturing (or 3D printing), the full potential of digital twin technologies will be unlocked, opening doors for new applications.
About the author:
Chandana Patnaik is a seasoned market research professional with 5+ years of experience in consulting and custom research projects. In her career, she has been a contributor to several renowned industry journals and contributes regularly to various technology magazines and portals. She finds her interest in writing about innovations or trends primarily concerning the Electronics and Semiconductor Industry, and she always strives to bring a unique blend of practical insights and industry expertise to her writings.
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like




